what was one way the renaissance changed society
The Renaissance: The 'Rebirth' of science & culture

The Renaissance, which means "rebirth" in French, typically refers to a flow in European history from A.D. 1400 to A.D. 1600. Many historians, all the same, assert that it started earlier or ended later on, depending on the country. It bridged the periods of the Middle Ages and modernistic history, and, depending on the country, overlaps with the Early Modern, Elizabethan and Restoration periods. The Renaissance is most closely associated with Italy, where it began in the 14th century, though countries such as Germany, England and French republic went through many of the same cultural changes and phenomena.
However, while the Renaissance brought well-nigh some positive changes for Europe, the geographical exploration that flourished during this time led to devastation for the people of the Western Hemisphere as European conquest and colonization brought plagues and slavery to the Indigenous people living at that place. In Africa, information technology also brought about the birth of the trans-Atlantic slave trade that saw Blackness people shipped from Africa to the Western Hemisphere to piece of work as slaves on European colonies.
"Renaissance" comes from the French word for "rebirth." According to the City Academy of New York at Brooklyn, intense interest in and learning about classical antiquity was "reborn" after the Center Ages, in which classical philosophy was largely ignored or forgotten. Renaissance thinkers considered the Center Ages to take been a period of cultural decline. They sought to revitalize their culture through re-emphasizing classical texts and philosophies. They expanded and interpreted them, creating their own style of art, philosophy and scientific enquiry. Some major developments of the Renaissance include astronomy, humanist philosophy, the printing press, vernacular language in writing, painting and sculpture technique, earth exploration and, in the late Renaissance, Shakespeare's works.
What is the Renaissance?
Many historians, including U.K.-based historian and writer Robert Wilde, prefer to think of the Renaissance as primarily an intellectual and cultural motility rather than a historical menstruum. Interpreting the Renaissance every bit a time period, though convenient for historians, "masks the long roots of the Renaissance," Wilde told Alive Science.
During this time, interest in classical antiquity and philosophy grew, with some Renaissance thinkers using it as a style to revitalize their culture. They expanded and interpreted these Classical ideas, creating their own style of art, philosophy and scientific research. Some major developments of the Renaissance include developments in astronomy, humanist philosophy, the printing press, vernacular language in writing, painting and sculpture technique, globe exploration and, in the late Renaissance, Shakespeare's works.
The term Renaissance was not commonly used to refer to the period until the 19th century, when Swiss historian Jacob Burckhardt popularized it in his archetype, "The Civilization of Renaissance Italy" (Dover Publications, 2022).
Historical development
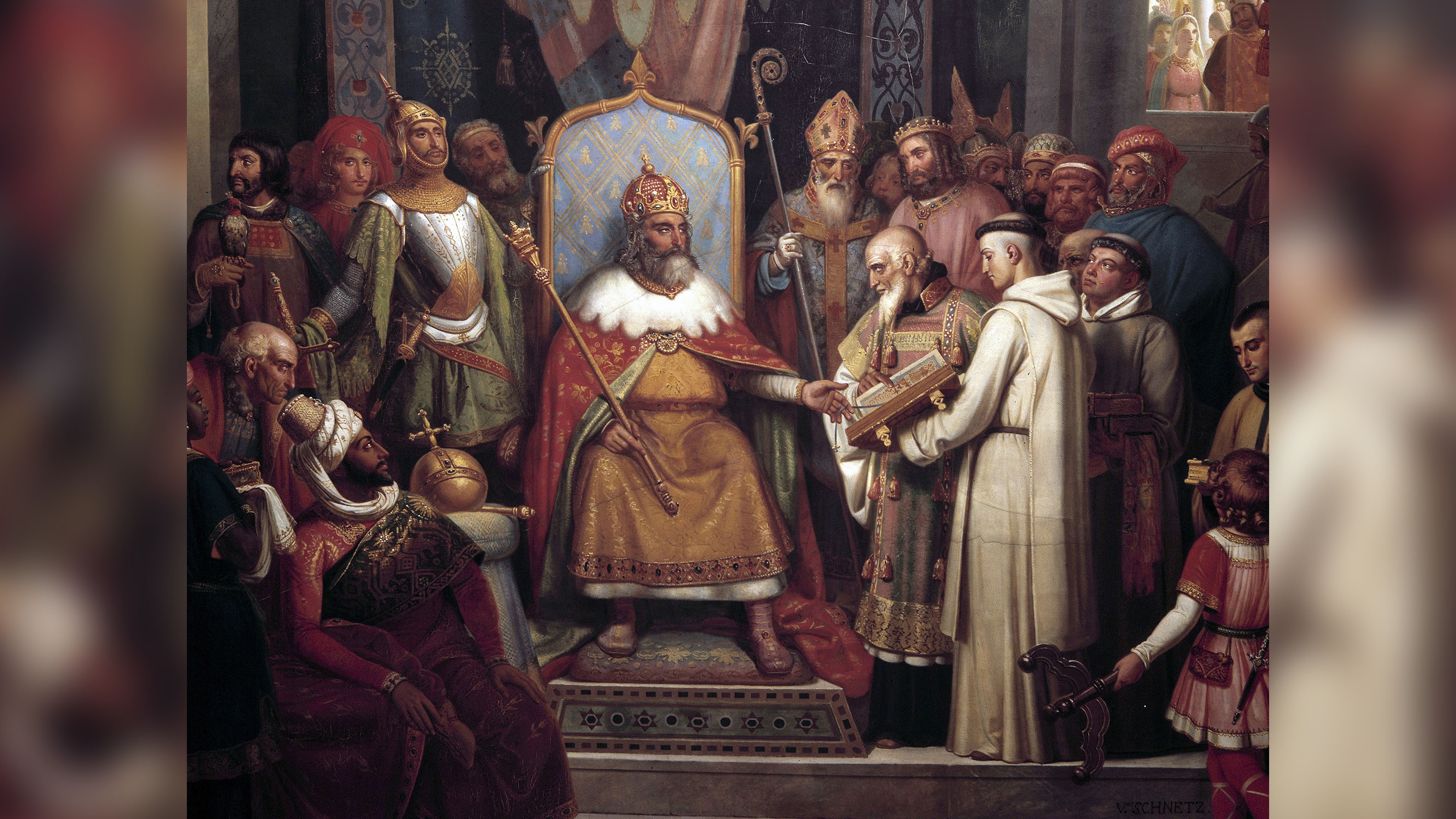

Contrary to popular belief, classical texts and knowledge never completely vanished from Europe during the Middle Ages. Charles Homer Haskins wrote in "The Renaissance of the Twelfth Century" (Harvard University Printing, 1927) that at that place were three principal periods that saw resurgences in the art and philosophy of antiquity: the Carolingian Renaissance, which occurred during the reign of Charlemagne, the first emperor of the Holy Roman Empire (eighth and ninth centuries), the Ottonian Renaissance, which developed during the reigns of emperors Otto I, Otto Ii and Otto Iii (10th century) and the 12th century Renaissance.
The 12th century Renaissance was especially influential on the afterward Renaissance, said Wilde. Europeans at the time studied on a larger scale Classical Latin texts and Greek science and philosophy; they also established early versions of universities.
The Crusades played a role in ushering in the Renaissance, Philip Van Ness Myers wrote in "Medieval and Modern History" (Ginn & Company, 1902). While crusading, Europeans encountered advanced Eye Eastern civilizations, which had made strides in many cultural fields. Islamic countries kept many classical Greek and Roman texts that had been lost in Europe, and they were reintroduced through returning crusaders.
The fall of the Byzantine Empire at the hands of the Ottomans also played a role. "When the Ottomans sacked Constantinople in 1453, many scholars fled to Europe, bringing classical texts with them," Susan Abernethy, a Colorado-based historian and author, told Live Science. "Conflict in Spain between the Moors and Christians too caused many academics to escape to other areas, particularly the Italian city-states of Florence, Padua and others. This created an atmosphere for a revival in learning."
The Blackness Decease helped fix the stage for the Renaissance, wrote Robert S. Gottfried in "The Black Expiry" (Simon and Schuster, 2022). Deaths of many prominent officials acquired social and political upheaval in Florence, where the Renaissance is considered to have begun. The Medici family moved to Florence in the wake of the plague and over the centuries produced business organisation and political leaders also equally four popes.
The Medici'southward, and many others, took advantage of opportunities for greater social mobility. Becoming patrons of artists was a pop way for such newly powerful families to demonstrate their wealth. Some historians also fence that the Black Expiry caused people to question the church's accent on the afterlife and focus more on the present moment, which is an element of the Renaissance'due south humanist philosophy.
Many historians consider Florence to be the Renaissance's birthplace, though others widen that designation to all of Italia. From Italy, Renaissance thought, values and creative technique spread throughout Europe, according to Van Ness Myers. Military invasions in Italy helped spread ideas, while the finish of the Hundred Years State of war betwixt France and England immune people to focus on things besides disharmonize.
The term "Renaissance Man," which is used today to describe someone who is talented in multiple fields, is derived from the Italian word "Uomo Universale," which means "universal human" and is oftentimes used to describe individuals like Leonardo da Vinci who thrived in multiple fields similar fine art and science.
Characteristics of the Renaissance
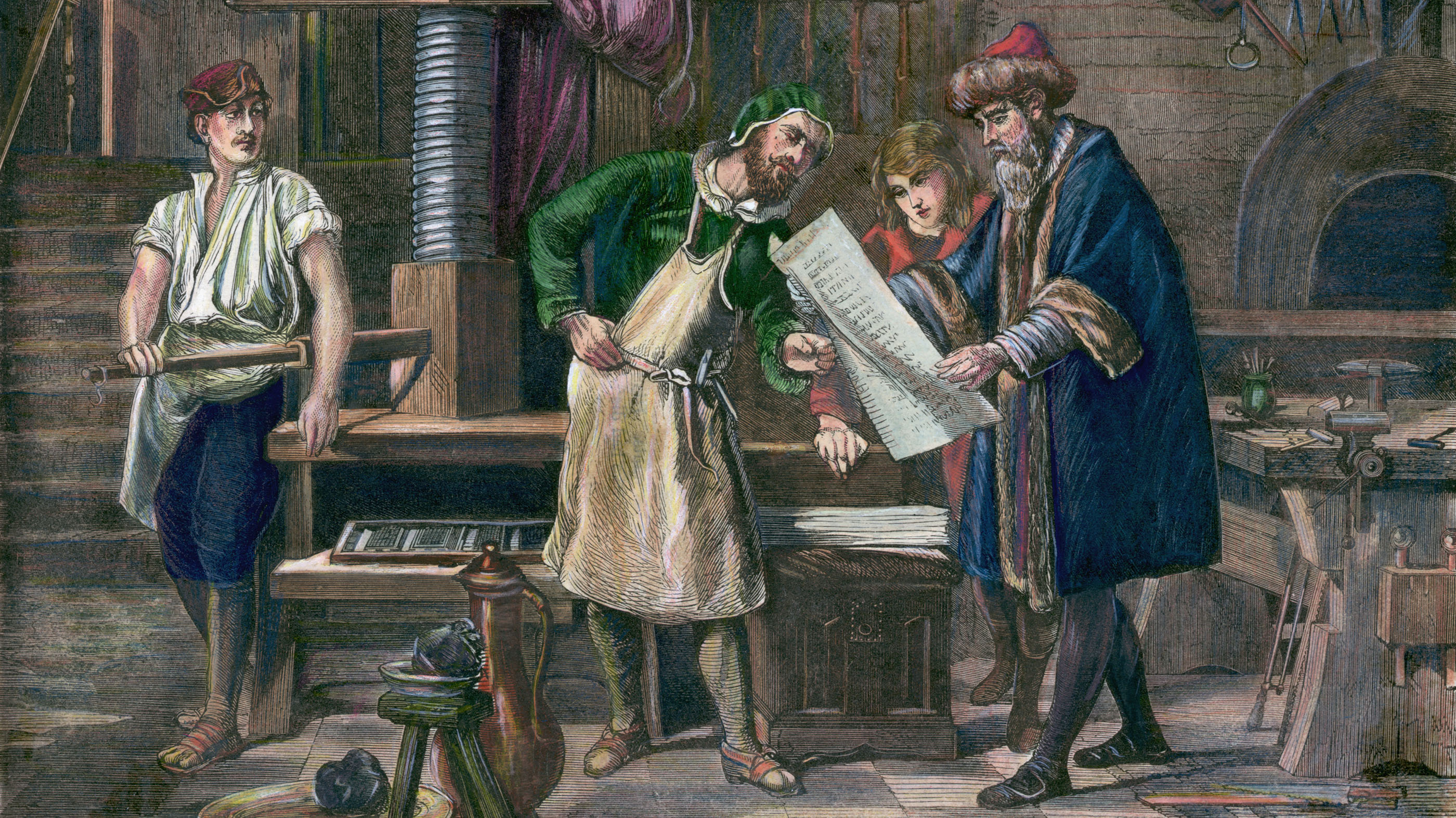

The development and growth of the printing press was perchance the nearly of import technical achievement of the Renaissance. Johannes Gutenberg developed it in 1440, although the technology was used in Cathay centuries earlier. It immune Bibles, secular books, printed music and more to be fabricated in larger quantities and reach more people. "The demand for perfect reproductions of texts and the renewed focus on studying them helped trigger ane of the biggest discoveries in the whole of human history: printing with movable type. For me, this is the easiest and single greatest evolution of the Renaissance and allowed modernistic culture to develop," said Wilde.
Intellectual movement
Wilde said one of the most meaning changes that occurred during the Renaissance was the "evolution of Renaissance humanism equally a method of thinking. … This new outlook underpinned then much of the world then and at present."
Renaissance humanism, Wilde said, involved "attempts by man to chief nature rather than develop religious piety." Renaissance humanism looked to classical Greek and Roman texts to change contemporary thought, assuasive for a new mindset after the Middle Ages. Renaissance readers understood these classical texts as focusing on human decisions, deportment and creations, rather than unquestioningly following the rules set forth by the Catholic Church as "God's plan."
Though many Renaissance humanists remained religious, they believed God gave humans opportunities, and it was humanity's duty to do the best and nearly moral beings. Renaissance humanism was an "ethical theory and practice that emphasized reason, scientific research and human fulfillment in the natural world," said Abernethy.
Renaissance art
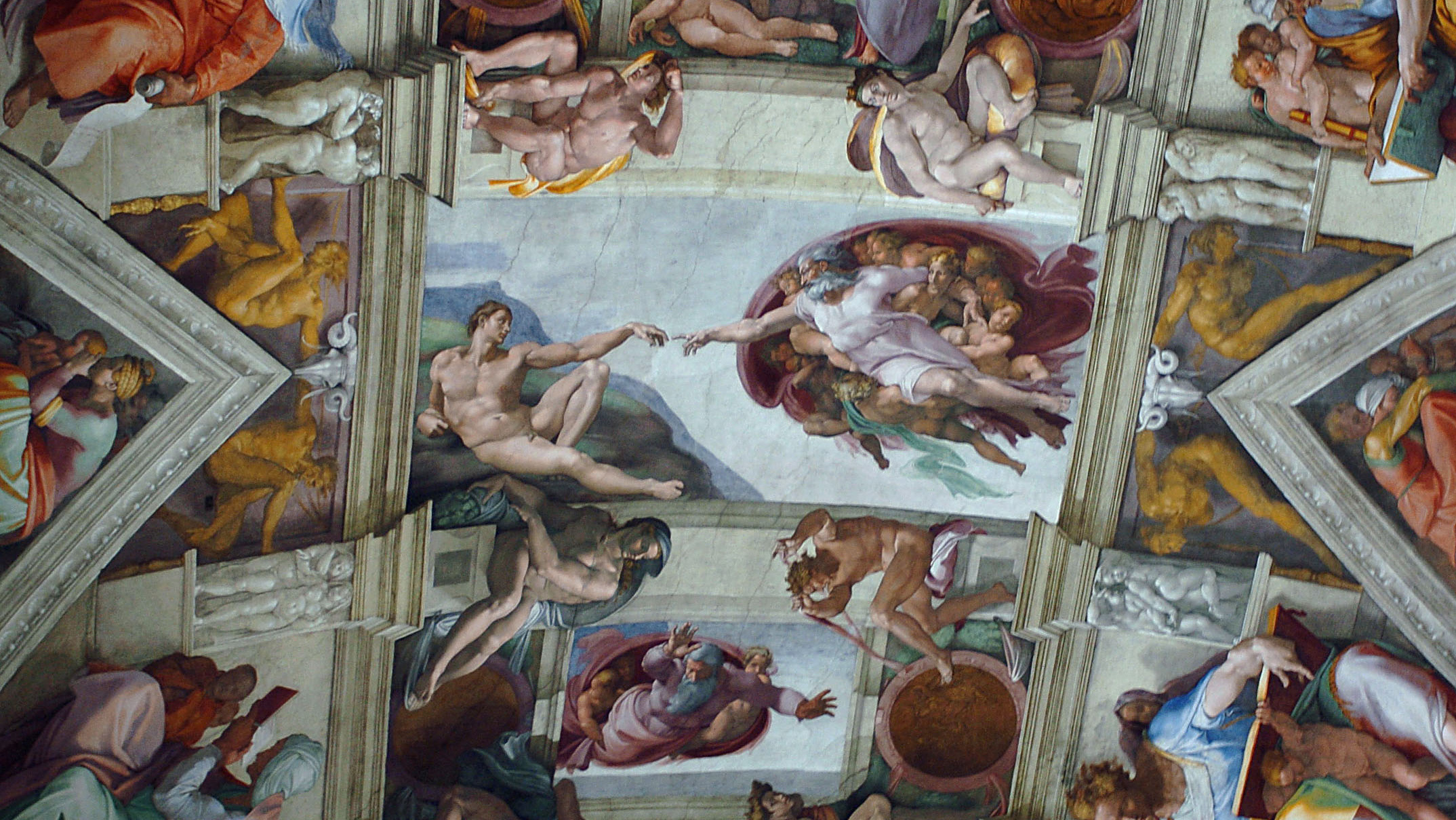

Renaissance art was heavily influenced by classical art, wrote Virginia Cox in "A Brusk History of the Italian Renaissance" (I.B. Tauris, 2022). Artists turned to Greek and Roman sculpture, painting and decorative arts for both inspiration and the fact that the techniques meshed with Renaissance humanist philosophy. Both classical and Renaissance art focused on human beauty and nature. People, even when in religious works, were depicted living life and showing emotion. Perspective, as well as low-cal and shadow techniques improved; and paintings looked more than three-dimensional and realistic.
Patrons made information technology possible for successful Renaissance artists to work and develop new techniques. The Catholic Church building commissioned most artwork during the Middle Ages, and while it continued to do and then during the Renaissance, wealthy individuals too became important patrons, co-ordinate to Cox. The most famous patrons were the Medici family in Florence, who supported the arts for much of the 15th and 16th centuries. The Medici family supported artists such every bit Michelangelo, Botticelli, da Vinci and Raphael.
Florence was the initial epicenter of Renaissance art, just by the finish of the 15th century, Rome had overtaken it. Pope Leo Ten (a Medici) ambitiously filled the city with religious buildings and fine art. This period, from the 1490s to the 1520s, is known equally the High Renaissance.
Renaissance music
Every bit with art, musical innovations in the Renaissance were partly made possible because patronage expanded beyond the Catholic Church. According to theMetropolitan Museum of Art, new technologies resulted in the invention of several new instruments, including the harpsichord and violin family. The printing press meant that sheet music could exist more widely disseminated.
Renaissance music was characterized past its humanist traits. Composers read classical treatises on music and aimed to create music that would bear upon listeners emotionally. They began to contain lyrics more dramatically into compositions and considered music and poetry to exist closely related, according to the Metropolitan Museum of Fine art.
Renaissance literature & theatre
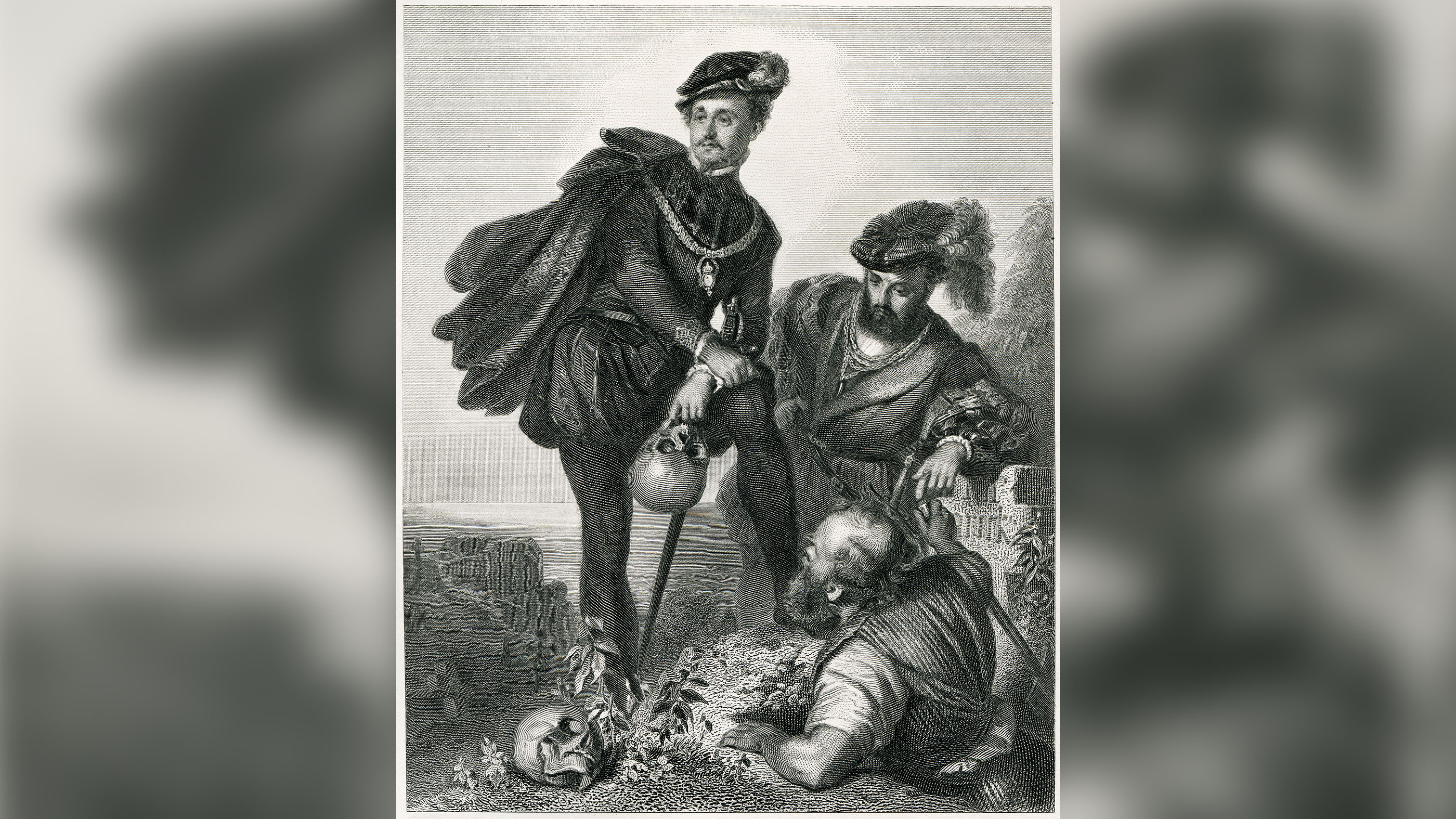

Renaissance literature, too, was characterized past humanist themes and a return to classical ideals of tragedy and comedy, according to the Brooklyn College English language Department. Shakespeare's works, especially "Hamlet," are good examples of this. Themes like human agency, life'southward non-religious meanings and the true nature of man are embraced, and Hamlet is an educated Renaissance man.
The press press allowed for popular plays to be published and re-dperformed around Europe and the world. A play's popularity oft determined whether publishers chose to print the script, wrote Janet Clarke, an emeritus professor of Renaissance Literature at the University of Hull, U.Chiliad., in her book "Shakespeare'southward Stage Traffic" (Cambridge University Press, 2022). "Publishers invested in plays that were pop as theatre traffic equally much as they invested in the authors" wrote Hull.
Renaissance society & economics
The most prevalent societal change during the Renaissance was the fall of bullwork and the rise of a capitalist market economy, said Abernethy. Increased trade and the labor shortage caused by the Blackness Death gave rise to something of a middle grade. Workers could need wages and good living weather, and so serfdom ended.
"Rulers began to realize they could maintain their ability without the church building. There were no more knights in service to the king and peasants in service to the lord of the manor," said Abernethy. Having coin became more important than your allegiances.
This shift frustrated popes. The "Peace of Westphalia," a series of treaties signed in 1648, fabricated it harder for the pope to interfere in European politics. Pope Innocent X responded that it was "null, void, invalid, iniquitous, unjust, damnable, reprobate, inane, and devoid of significant for all time."
Renaissance religion
Due to a number of factors — including the Black Death, the rising in trade, the development of a centre class and the papacy's temporary move from Rome to Avignon (1309 to 1377) — the Catholic Church'due south influence was waning as the 15th century began. The re-emergence of classical texts and the rise in Renaissance humanism changed social club's approach to faith and the potency of the papacy, said Abernethy. "[Humanism] created an atmosphere that gave rise to different movements and sects … Martin Luther stressed reform of the Catholic Church, wanting to eliminate practices such as nepotism and the selling of indulgences," Abernethy said.
"Peradventure well-nigh important, the invention of the printing printing allowed for the dissemination of the Bible in languages other than Latin," Abernethy connected. "Ordinary people were at present able to read and learn the lessons of Scripture, leading to the Evangelical motion." These early Evangelicals emphasized the importance of the scriptures rather than the institutional power of the church and believed that salvation was personal conversion rather than being determined by indulgences or building works of fine art or architecture.
The fracturing of Christians in western Europe into different groups led to conflicts, sometimes called the "wars of religion," that lasted for centuries in Europe. These conflicts sometimes led groups of people to go out Europe in hopes of avoiding persecution. I of these groups would become known equally the Pilgrims when they came to Plymouth in 1620.
Renaissance geography
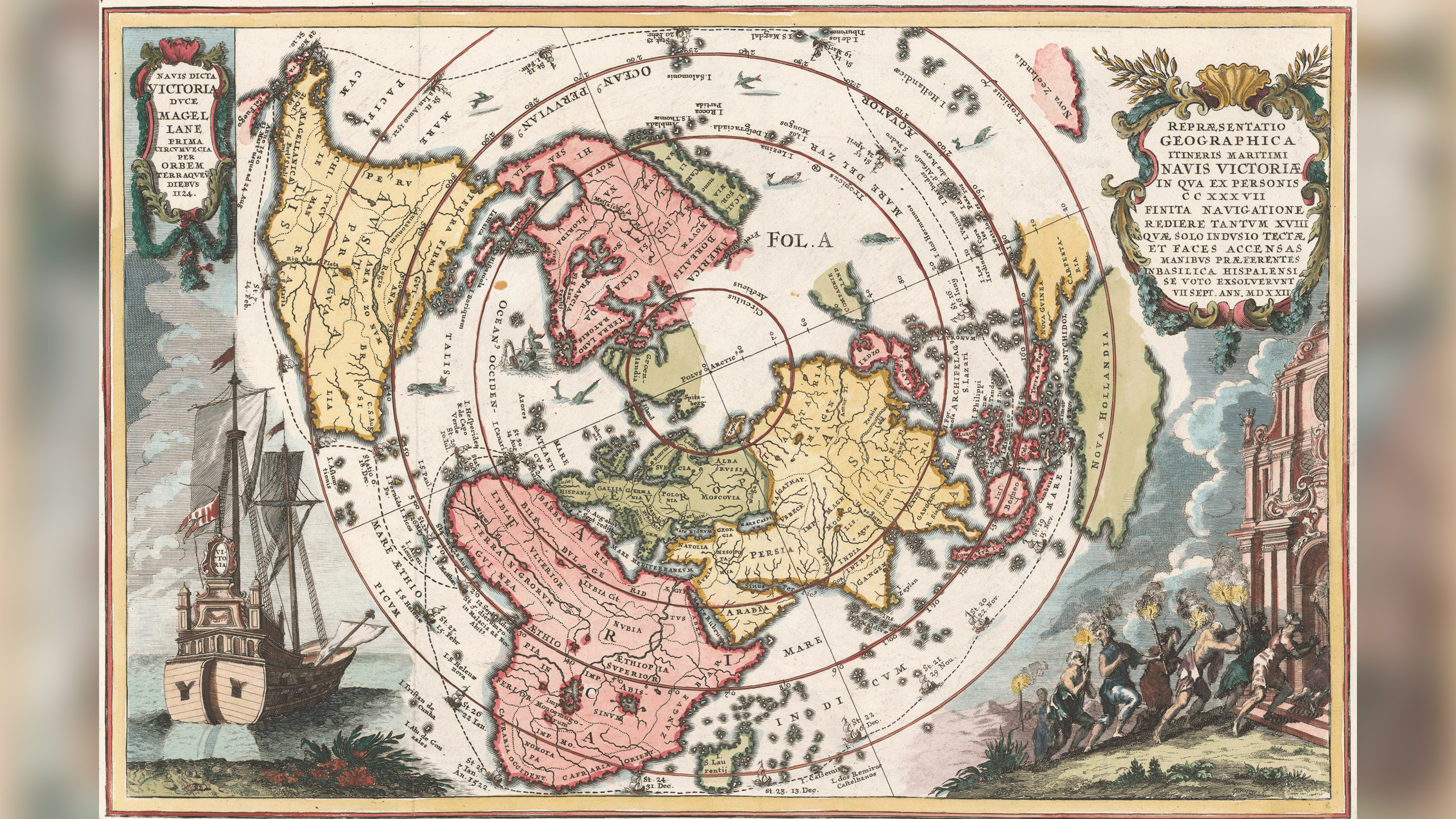
Thirsty to learn more well-nigh the world and eager to better trade routes, explorers sailed off to chart new lands. Columbus "discovered" the New World in 1492, and Ferdinand Magellan became the showtime person to successfully circumnavigate the globe in the early 1500s.
For the people of the Western Hemisphere, the European exploration and colonization that occurred was disastrous. With little or no amnesty to the diseases Europeans brought over, the Indigenous population was ravaged by plagues, with expiry rates in some areas estimated as high as 90%. The Spanish conquered the Aztec and Inca Empires, forcing the native survivors to work as slaves.
European powers too explored more of Africa, starting to conquer and colonize parts of the continent. As their force in Africa grew, Europeans began to accept people from Africa to work as slaves — in some cases sending them to piece of work on colonies in the Caribbean area and South America — this trans-Atlantic slave trade eventually expanding to what is now the U.s.a..
Renaissance science
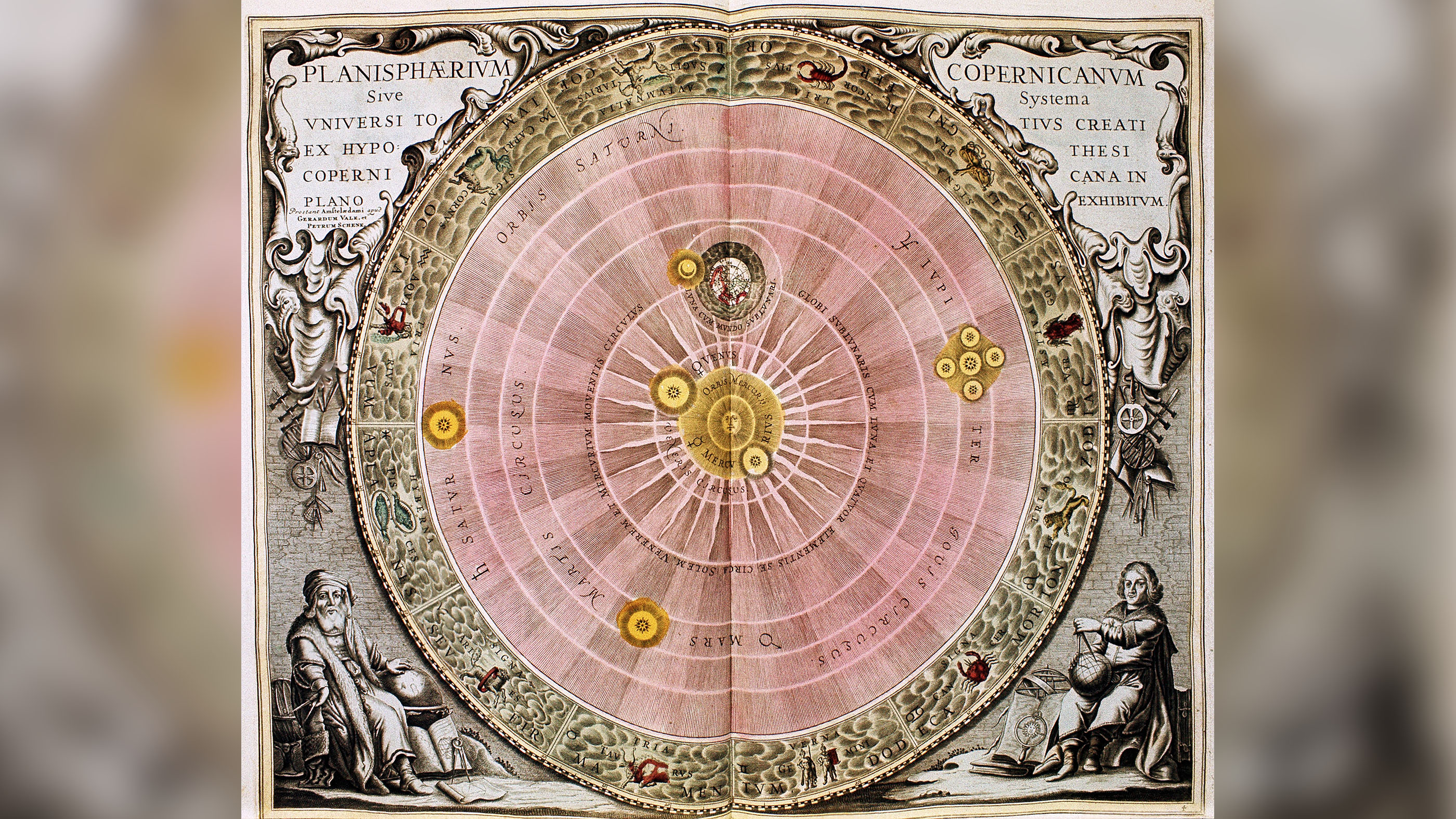
Every bit scholars studied classical texts, they "resurrected the ancient Greek belief that creation was constructed effectually perfect laws and reasoning," Abernethy said. "At that place was an escalation in the study of astronomy, anatomy and medicine, geography, alchemy, mathematics and architecture as the ancients studied them."
One of the major scientific discoveries of the Renaissance came from Polish mathematician and astronomerNicolaus Copernicus. In the 1530s, he published his theory of a heliocentric solar arrangement. This places the sun, not the World, at the center of the solar system. Information technology was a major breakthrough in the history of scientific discipline, though the Catholic Church building banned the printing of Copernicus' book.
Empiricism began to catch scientific thought. "Scientists were guided by experience and experiment and began to investigate the natural world through observation," said Abernethy. "This was the commencement indication of a divergence between science and religion. … They were beingness recognized every bit ii divide fields, creating conflict between the scientists and the church, and causing scientists to be persecuted," continued Abernethy. "Scientists constitute their work was suppressed or they were demonized equally charlatans and accused of dabbling in witchcraft, and sometimes existence imprisoned."
Galileo Galilei was a major Renaissance scientist persecuted for his scientific experiments. Galileo improved the telescope, discovered new angelic bodies and found support for a heliocentric solar system. He conducted motion experiments on pendulums and falling objects that paved the style for Isaac Newton'south discoveries about gravity. The Cosmic Church forced him to spend the final nine years of his life under house abort.
Renaissance festival
While the term "Renaissance festival" typically refers to modern-day festivals that celebrate the fine art and culture of the Renaissance, there were festivals that took place during the Renaissance itself.
For case, Henri Two, who was rex of France between 1547 and 1559, held festivals periodically throughout his reign that included stages of performers and lengthy parades. The festivals included the arrivals of the male monarch into the urban center or town where the festival was being held, wrote Richard Cooper, an emeritus professor of French at the Academy of Oxford, in a newspaper published in the book "Court Festivals of the European Renaissance" (Taylor & Francis, 2022). Henri II sometimes held these festivals to make an of import upshot such as the coronation of his queen or a military victory, wrote Cooper.
How the Renaissance changed the world
"The Renaissance was a time of transition from the ancient world to the modernistic and provided the foundation for the birth of the Age of Enlightenment," said Abernethy. The developments in science, fine art, philosophy and trade, as well every bit technological advancements like the press press, left lasting impressions on society and prepare the stage for many elements of our modern culture.
However, while the Renaissance had some positive affect for Europe, it had devastating impacts for people of the Western Hemisphere, equally plagues decimated Indigenous populations and the survivors often constitute themselves enslaved and under the dominion of European colonizers. This system of conquest, colonization and slavery also repeated itself in Africa as European ability grew. Today, the ramifications of European colonization and slavery are still felt and hotly debated effectually the world.
Additional resources
—Larn more well-nigh the geniuses of the Renaissance, from da Vinci and Galileo to Descartes and Chaucer on this History Channel page, with links to biographies of each.
—In this volume by author Catherine Fet, kids will acquire nigh the Renaissance and its characters through tales of adventure.
—In this 4-part BBC Idiot box series called "Renaissance Unchained," Waldemar Januszczak gives you a peek inside the more than exciting aspects of the time, from an episode on the gods and myths to 1 on a catamenia of war, confusion and … "darkness."
Bibliography
"The Civilization of the Renaissance in Italy Paperback" past Jacob Burckhardt, Dover Publications, September 16, 2022. https://world wide web.amazon.com/dp/0486475972
"The Renaissance of the 12th Century" by Charles Homer Haskins, Harvard Academy Press, 1927. https://www.amazon.com/dp/0674760751
"The Black Death: Natural and Homo Disaster in Medieval Europe" by Robert S. Gottfried, Free Press, March one, 1985. https://www.amazon.com/Black-Death-Natural-Disaster-Medieval/dp/0029123704
"A Short History of the Italian Renaissance" past Virginia Cox, I.B. Tauris, 2022. https://world wide web.amazon.com/History-Italian-Renaissance-I-B-Tauris-Histories/dp/1784530778
"Music in the Renaissance" at the Metropolitan Museum of Art. https://world wide web.metmuseum.org/toah/hd/renm/hd_renm.htm
Introduction to the Renaissance past the Brooklyn Higher English Section. http://academic.brooklyn.cuny.edu/english/melani/cs6/ren.html
Philip Van Ness Myers wrote in "Medieval and Modern History" (Ginn & Company, 1902). https://www.amazon.com/Mediaeval-Modern-History-Philip-Centre/dp/B001R6ARQI
Source: https://www.livescience.com/55230-renaissance.html
Posted by: xiongbefornes.blogspot.com


0 Response to "what was one way the renaissance changed society"
Post a Comment